多继承和魔法方法
在上一节中,我们讲了类的定义,属性和方法,那么我们这个节课来看看多继承和魔法方法。
多继承
在上节我们讲到了继承,一个类可以继承一个类,继承之后可以把父类所有的方法和属性都直接继承过来,那一个类可以继承多个类呢?
如果可以继承多个类的话,那如果两个父类中有一样的方法的情况下,子类继承哪一个呢?
演示
1 | class Base: |
输出
1 | this is A |
首先类是可以多继承的
优先使用第一个类里面的方法。
总结
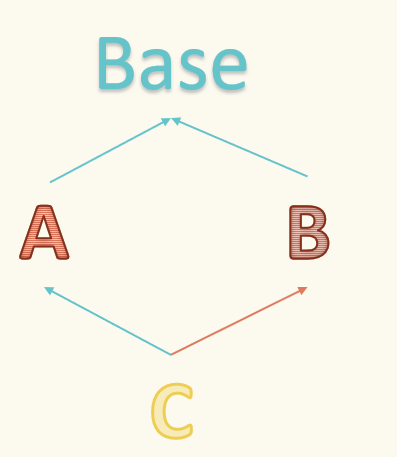
通过C类实例的方法调用来看
当继承多个父类时,如果父类中有相同的方法,那么子类会优先使用最先被继承的方法.
重构
在上面的例子中,如果不想继承父类的方法怎么办呢?
1 | class Base: |
输出
1 | this is C |
当子类继承父类之后,如果子类不想使用父类的方法,可以通过重写来覆盖父类的方法.
扩展
重写父类方法之后,如果又需要使用父类的方法呢?
方法一
1 | class Base: |
输出
1 | this is A |
方法二
1 | class Base: |
输出
1 | this is A |
super
super函数可以调用父类的方法
1 | class Base: |
输出
1 | this is Base |
那为什么是这个顺序输出呢?
1 | print(C.mro()) |
输出
1 | [<class '__main__.C'>, <class '__main__.A'>, <class '__main__.B'>, <class '__main__.Base'>, <class 'object'>] |
继承顺序:
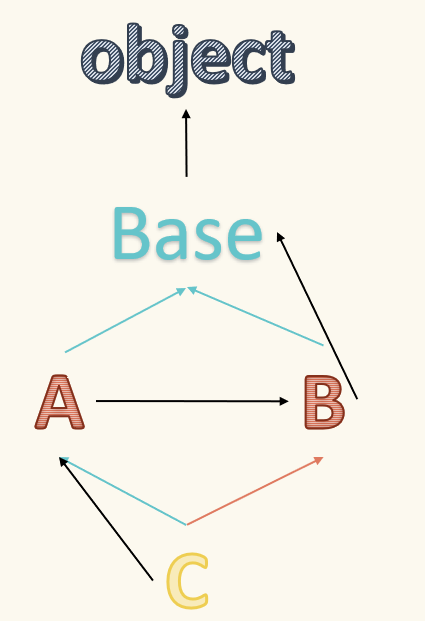
在python3中,类被创建时会自动创建方法解析顺序mro
object是所有类的父类
Mixin开发模式

Mixin是一种开发模式,一般规范上,Mixin类是继承的终点,即不再被继承
Mixin的优点就是不需要过多考虑继承关系,不会出现各父类之间有相同方法的情况
总结
mro: 类在生成时会自动生成方法解析顺序,可以通过 类名.mro()来查看
super: super函数可以来调用父类的方法,使用super的好处在于即使父类改变了,那么也不需要更改类中的代码
Mixin: Mixin是一种开发模式,给大家在今后的开发中提供一种思路.
魔法方法
在讲字符串拼接的时候,字符串可以直接相加,那我们自定义的类可以实现吗?
1 | class Rectangle: |
输出
(8, 10)
运算方法
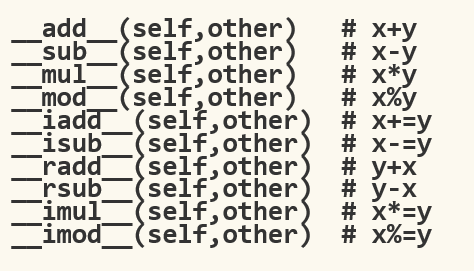
运算方法大家了解下就行,在实际运用中用不并不多。
add和radd原理
1 | class A: |
输出
1 | __radd__ |
优先在两类里找add方法,没有就自动调用radd方法。
演示
1 | class A: |
输出
1 | 246 |
str和repr原理
1 | class Rectangle: |
输出:
1 | # 有str |
优先在两类里找str方法,没有就自动调用repr方法。
在python中,str和repr方法在处理对象的时候,分别调用的是对象的str和repr方法
print也是如此,调用str函数来处理输出的对象,如果对象没有定义str方法,则调用repr处理
call方法
1 | class Rectangle: |
输出
1 | Rectangle called |
正常情况下,实例是不能像函数一样被调用的,要想实例能够被调用,就需要定义 call 方法
其他魔法方法

演示:
1 | class Rectangle: |
输出
1 | <class '__main__.Rectangle'> |
简单了解。
魔法方法应用场景
str和repr: str和repr都是分别调用这两个魔术方法来实现的
原理:在类中,很多事情其实调用的魔术方法来实现的
作用:通过合理的利用魔术方法,可以让我们更加方便的展示我们的数据
转载请注明:Seven的博客

